National Bureau of Economic Research
Latest from the NBER
A research summary from the monthly NBER Digest

Reallocation of Global Supply Chains
article
The structure of US international trade has undergone a dramatic transformation since 2018 when the US began imposing substantial tariffs targeting Chinese imports. This trade policy shift, combined with pandemic-era supply chain disruptions and subsequent geopolitical tensions, led US firms to reconsider their global sourcing strategies.
In An Anatomy of the Great Reallocation in US Supply Chain Trade (NBER Working Paper 34490), Laura Alfaro and Davin Chor analyze detailed product-level trade data from the US Census Bureau, examining over 5,300 product categories over the period 2017 to 2025. They combine this trade data with information on tariff rates, product characteristics such as capital ...
From the NBER Reporter: Research, program, and conference summaries

Program Report: Industrial Organization
article
Researchers in the Industrial Organization (IO) program study consumer and firm behavior, competition, innovation, and government regulation. This report begins with a brief summary of general developments in the last four decades in the range and focus of program members’ research, then discusses specific examples of recent work.
When the program was launched in the early 1990s, two developments had profoundly shaped IO research. One was the development of game-theoretic models of strategic behavior by firms with market power, summarized in Jean Tirole’s classic textbook. The initial wave of research in this vein was focused on applying new insights from economic theory; empirical applications came later. Then came the development of econometric methods to estimate demand and supply parameters in…
From the NBER Bulletin on Health

Pain Management and the Opioid Epidemic
article
Death rates due to drug poisonings began to surge in the US in the mid-1990s, marking the emergence of an epidemic that has persisted for three decades. The health consequences have been stark, with annual deaths exceeding 100,000 since 2021.
In Prescription for Disaster: The SSDI Rate, Pain, and Prescribing Practices (NBER Working Paper 34265), William N. Evans and Ethan M. J. Lieber examine characteristics of counties in 1990—prior to the surge—that predict the county-level severity of opioid deaths after 2000. After considering a wide range of potential determinants, they focus on one factor: the percentage of the working-age population...
From the NBER Bulletin on Entrepreneurship
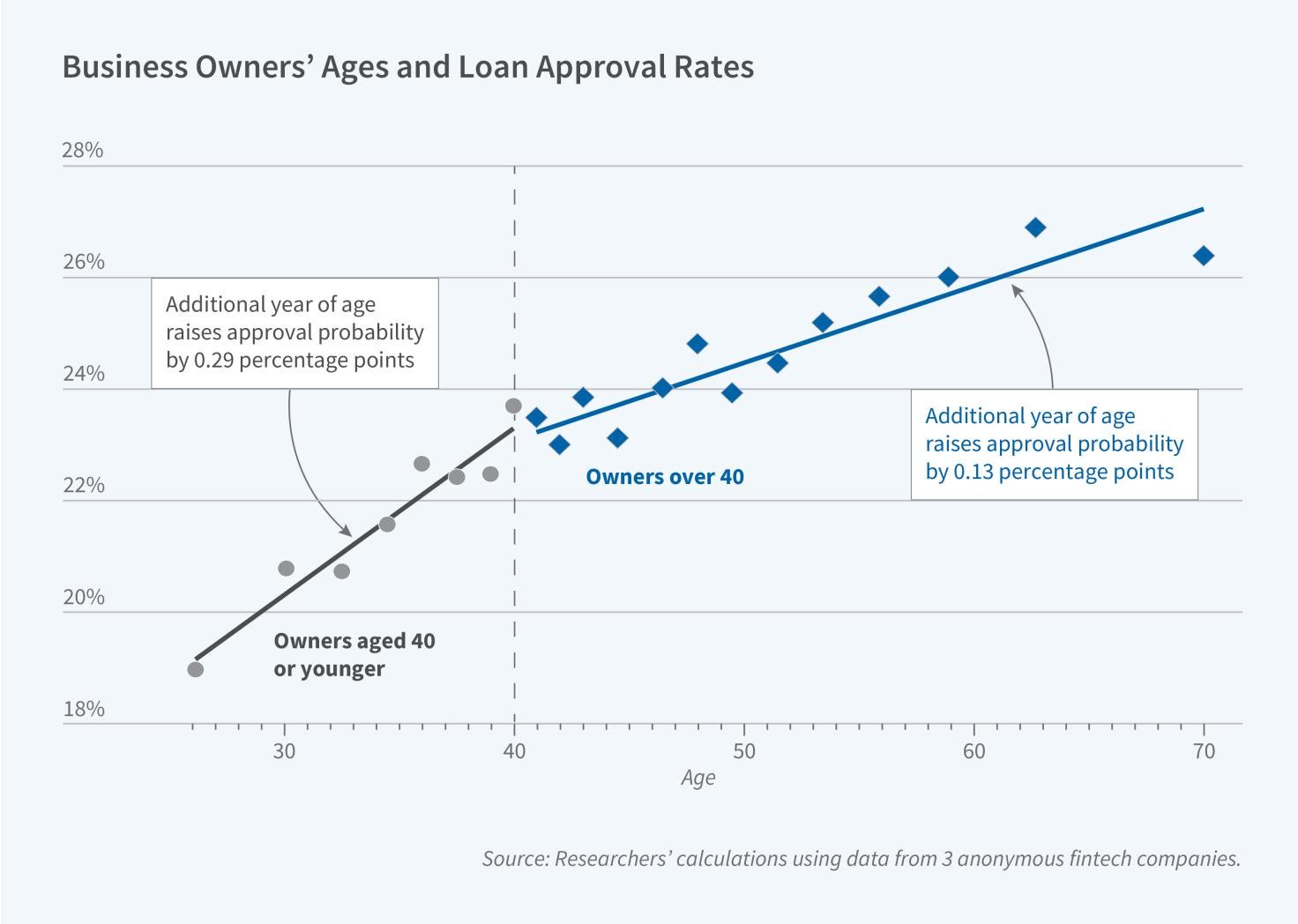
Underwriting Based on Cash Flow Helps Younger Entrepreneurs Access Credit
article
Younger entrepreneurs are disadvantaged in small business loan markets because lenders rely heavily on personal credit scores, which favor long histories of repaying debt. In Modernizing Access to Credit for Younger Entrepreneurs: From FICO to Cash Flow (NBER Working Paper 33367), researchers Christopher M. Hair, Sabrina T. Howell, Mark J. Johnson, and Siena Matsumoto document this fact and show that younger entrepreneurs benefit from underwriting that augments personal credit scores (like FICO) with cash flow data. They analyze comprehensive…
Featured Working Papers
Since 2022, Kalshi prediction-market forecasts for the federal funds rate have achieved perfect accuracy on the day before FOMC meetings, significantly outperforming federal funds futures, according to Anthony M. Diercks, Jared Dean Katz, and Jonathan H. Wright.
Jason B. Cook, Elizabeth Cox, and Chloe N. East find that SNAP work requirements for able-bodied adults without dependents increase procedural denials by 8 percentage points (22 percent), suggesting that work requirements deter participation among the eligible.
Geumbi Park, Xiaoqing Zhou, and Sarah Zubairy find that over 70 percent of Department of Defense subcontract spending between 2011 and 2024 crossed state lines. Accounting for this when estimating local economic multipliers for government spending raises the estimates by about 20 percent and reduces the cost per job from $400,000 to $330,000.
Student supervision that ensured consistent Khan Academy usage in 83 Indian schools increased student platform usage from 7 to 47 minutes per week and was associated with mathematics achievement gains of almost half a standard deviation over 31 weeks, according to Philip Oreopoulos, Oliver Keyes-Krysakowski, and Deepak Agarwal.
Low-income children born just before their state's preschool-entry cutoff are 17 percent and 9 percent more likely to be diagnosed with ADHD and speech or language disorders, respectively, and 27 percent more likely to receive school-based services at ages 3–4, compared to children born just after the cutoff, according to Maya Rossin-Slater, Adrienne Sabety and Aileen Wu.
In the News
Recent citations of NBER research in the media
_______________________________________
Research Projects
Conferences
Books & Chapters
Through a partnership with the University of Chicago Press, the NBER publishes the proceedings of four annual conferences as well as other research studies associated with NBER-based research projects.
Videos
Recordings of presentations, keynote addresses, and panel discussions at NBER conferences are available on the Videos page.